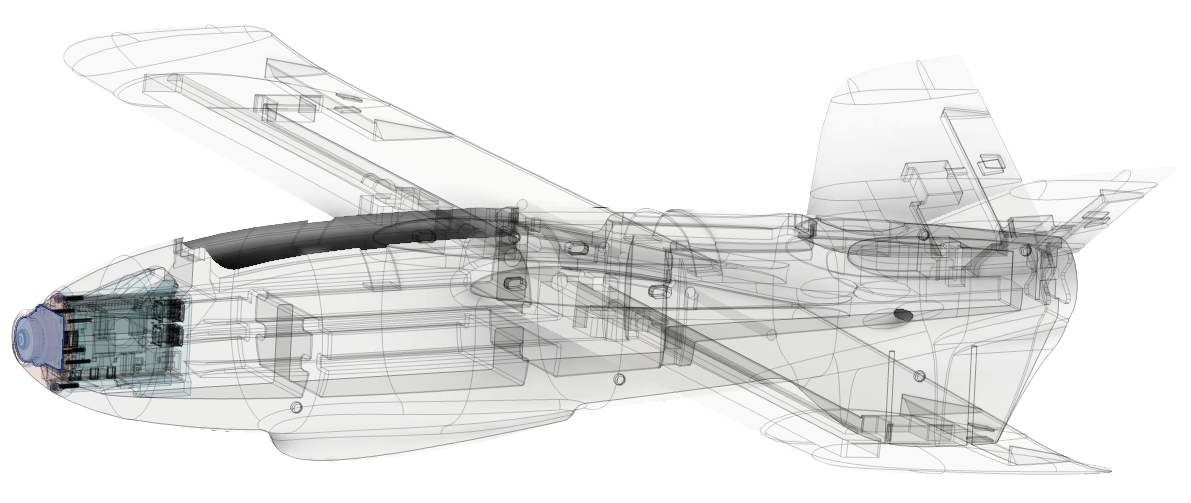
Autonomous Terminal Guidance for Small Fixed-Wing UAVs
Project Rundown
The use of autonomous terminal guidance technology significantly enhances reconnaissance, target acquisition, and direct engagement across various terrains. The system’s advanced AI and machine learning algorithms enable real-time processing, allowing the UAVs to adapt to dynamic combat conditions, even in complex environments. This precision reduces collateral damage and increases the likelihood of successful mission outcomes.
One of the standout features of this technology is its resistance to external electronic warfare systems. By leveraging onboard processing and vision-inertial odometry, the UAVs can operate independently of GPS signals, which are often targeted by electronic jamming. The advanced architecture and adaptive algorithms further enhance its capability to maintain operational integrity, ensuring reliable performance despite attempts to disrupt its functionality.








Technical Specifications
- Maximum Strike Distance: ~ 2000 m
- Maximum Strike Altitude: Up to 400 m
- Maximum Operational Wind Speed: 10 m/s
- Guidance Law: Visual Guidance
- Robustness to Environmental Factors: Less resistant to turbulence; resistant to wind
- Command Processing Latency: 20 m/s
Hardware Overview
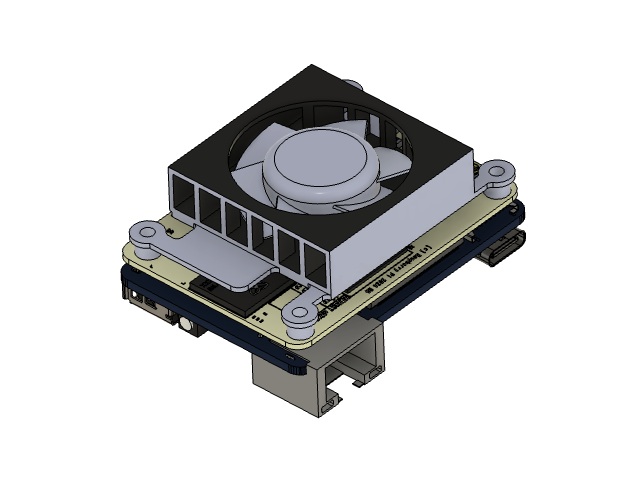
- Communication with the flight controller occurs via the MAVLink protocol, transmitting simulated readings generated by the module.
- An alternative method is full flight control using RC commands via UART from the onboard computer to the controller.
VIO Module Components:
- Raspberry PI5
- Raspberry Pi Camera
- Power Module
Upcoming Developments
Integration of Thermal Imaging and Night Vision Cameras: Additional adaptation of the algorithm is required to ensure reliable system performance during nighttime and low-visibility conditions.
Maneuvering Target Tracking: Enhancing the system’s capability to accurately capture and track moving, complex targets, including the identification and designation of specific points for engagement.
Extended Autonomous Operation: Ensuring the system’s full autonomous functionality, allowing it to search and identify the target fully operate independently without requiring communication with a human operator.