Autonomous Interception of Aerial Targets
Project Rundown
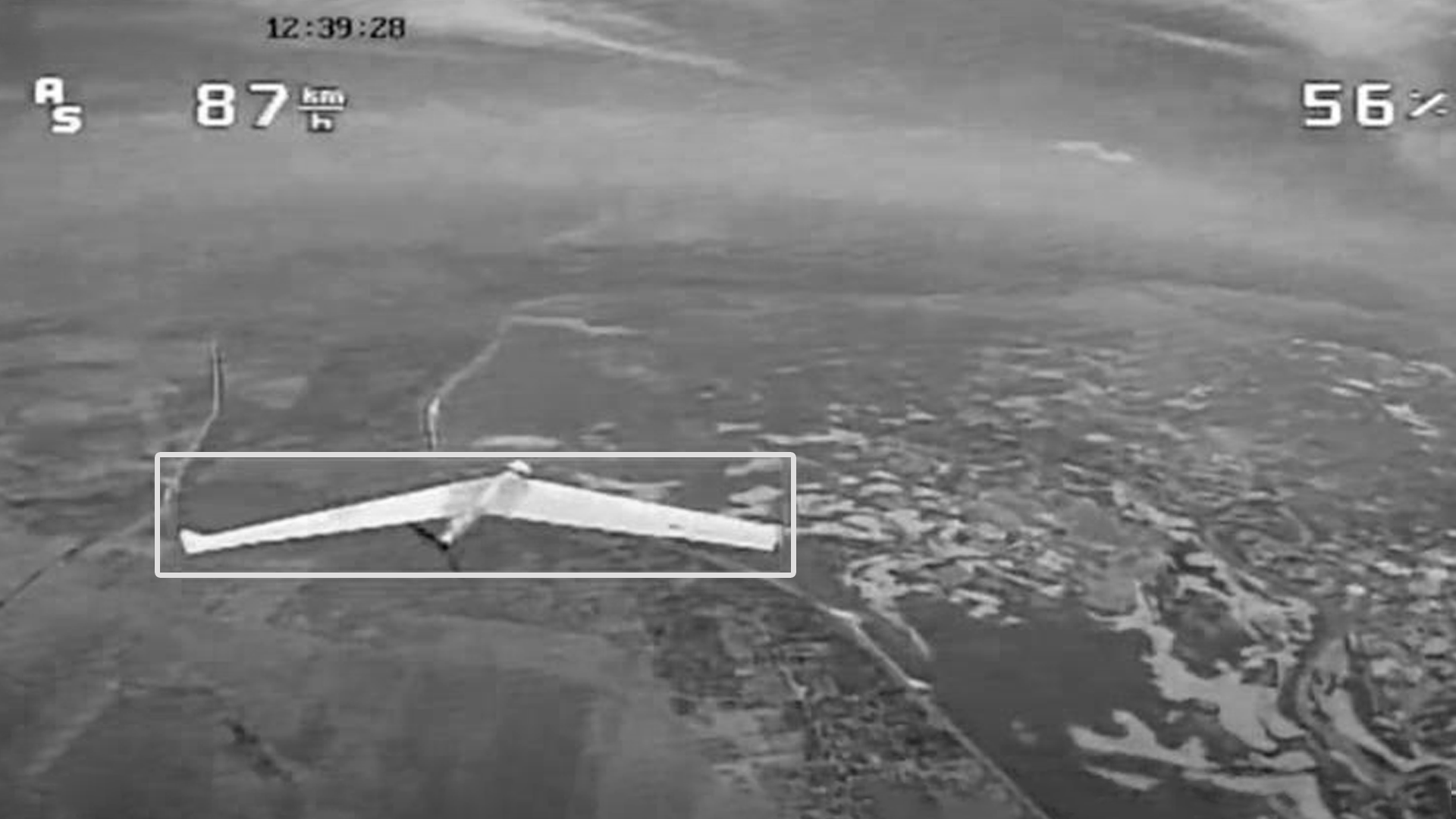
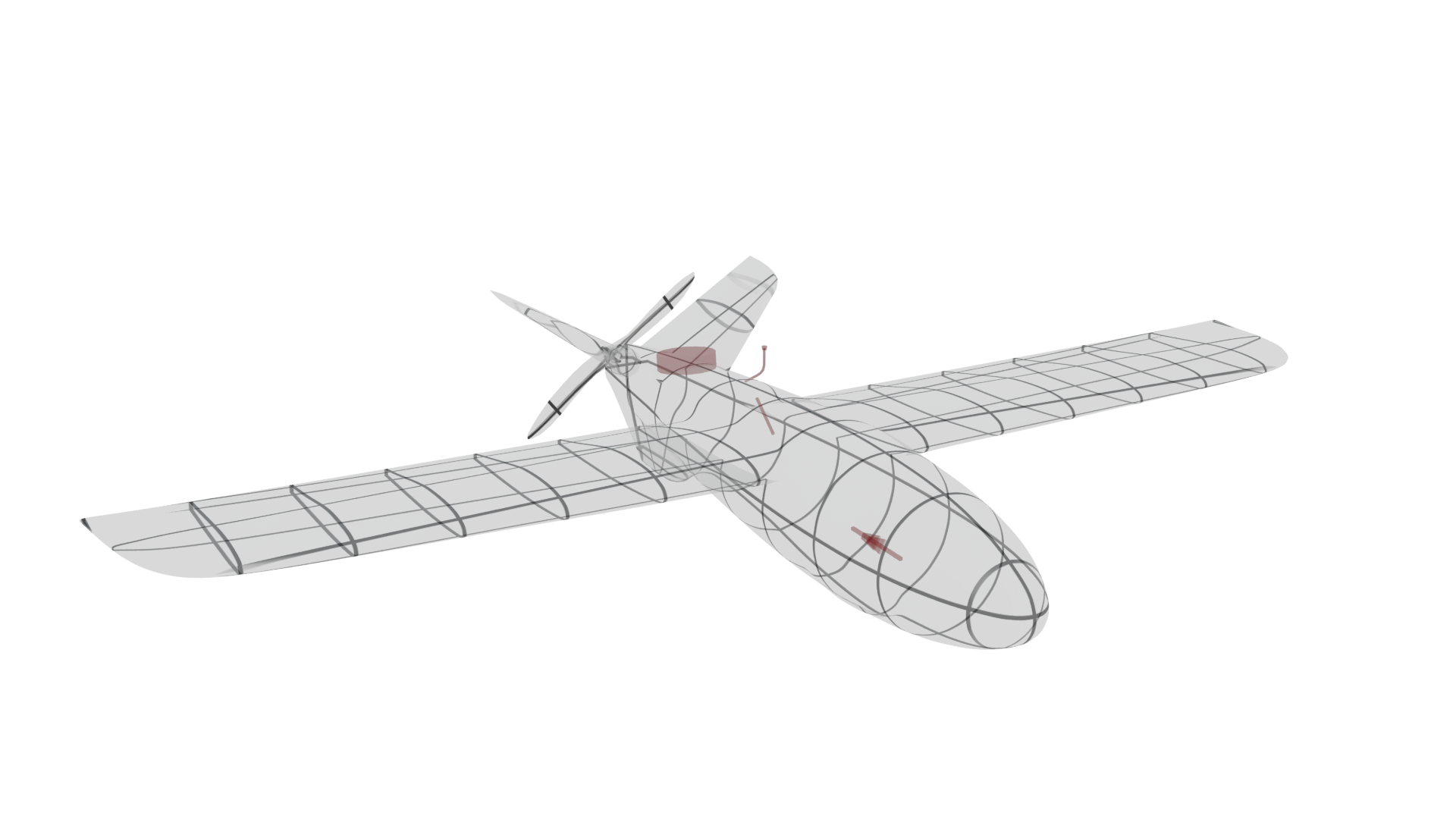
The Interceptor is a lightweight, software-driven aerial platform built around a small fixed-wing UAV, designed for autonomous or semi-autonomous interception of aerial threats. At its core is a vision-based targeting module powered by neural networks, enabling real-time detection, classification, and continuous optical tracking of fast-moving targets – even in GPS-denied or electronically contested environments.
The system integrates a Raspberry Pi-based onboard computer and a digital camera to perform detection and guidance tasks independently of GNSS. Enhanced with deep learning and sensor fusion, the computer vision engine filters out false positives and decoys. Once a target is visually acquired, the UAV autonomously adjusts its trajectory for interception. While tracking and guidance are fully automated, final engagement remains under human authorization, providing a critical layer of control and accountability.
Currently integrated with Ardupilot, the modular software stack is adaptable to a variety of airframes with appropriate calibration. This architecture delivers a balanced, high-performance counter-drone solution suitable for dynamic defense scenarios with minimal operator input.






Technical Specifications
- Visual Target Detection
- Maneuverable Target Tracking
- Autonomous Lock-on
- Dynamic Trajectory Adjustment
- Radar-cued Initial Guidance
- Target Engagement Range: Up to 500 m
- Optical / Digital Zoom: 4× optical, 15× digital
- Sensor Resolution: 640×512 (thermal) or 4K (daylight)
- Frame Rate: ≥30 fps for smooth, real-time tracking
Implementation Overview
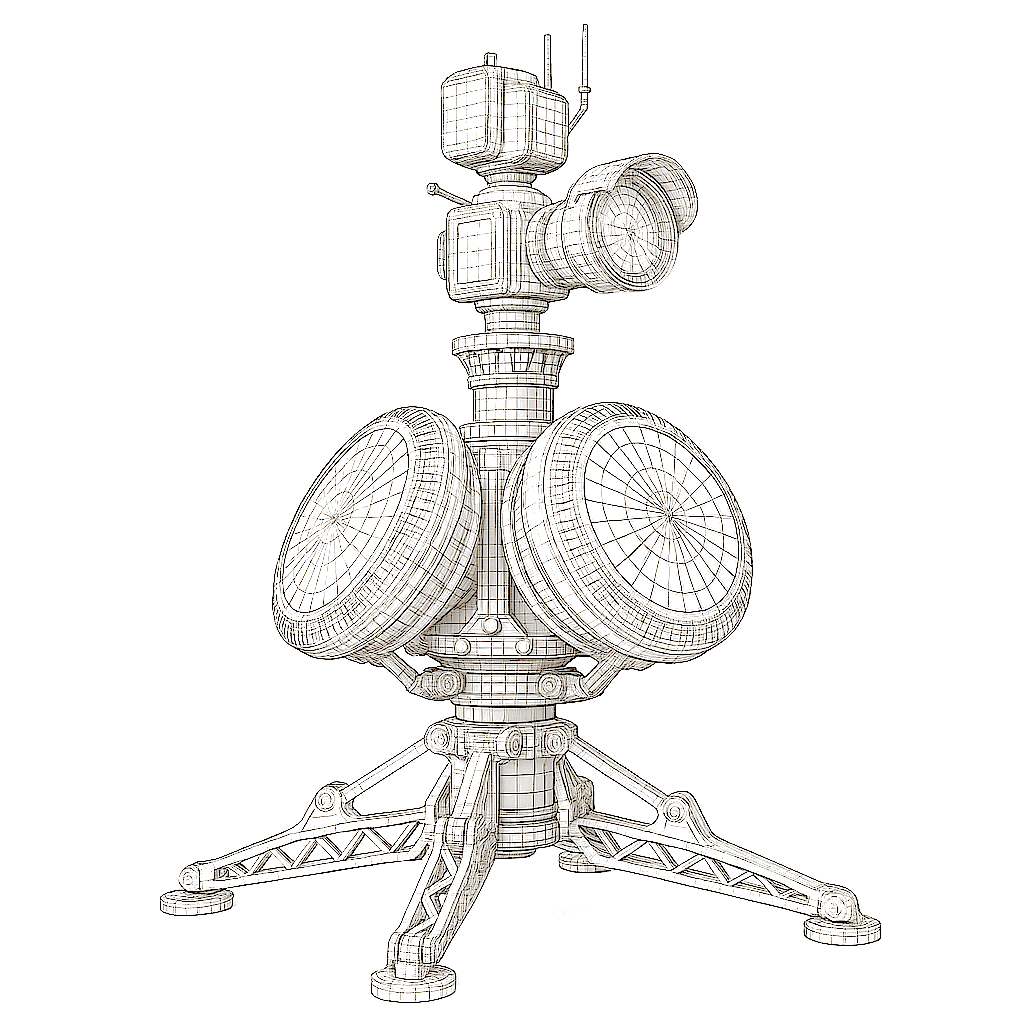
Vision Systems:
- 12 MP daylight camera for high-detail visual tracking
- High-resolution LWIR night vision camera for low-light environments
- Thermal camera for accurate heat-based target detection
- Neural network-based object detection (powered by YOLO architecture)
Processing Unit:
- Onboard low-powered dedicated AI processor
- Low-latency control loop for effective interception
Sensor Fusion Module:
- Combines vision and inertial sensors to enhance situational awareness
- Supports MAVLink and UART communication with flight controller
Guidance & Navigation:
- Preliminary target alignment using commands from tactical radars
- Detection of maneuvering targets, visual tracking, and terminal guidance
Communication:
- Supports both analog and digital links between the interceptor and ground control
- Additional functions controlled via standard RC transmitter
Applications
The Interceptor is optimized for neutralizing a wide range of unmanned aerial threats:
- Reconnaissance Drones: Disrupts intelligence-gathering operations by visually detecting and tracking low-observable UAVs.
- Strike Drones: Engages and intercepts weaponized drones before they reach critical targets.
- Loitering Drones: Eliminates slow-moving or hovering UAVs that evade radar and are often used for target acquisition or delayed attacks.
This technology excels in mobile perimeter defense, convoy protection, frontline surveillance interdiction, and various other tactical operations. It provides a reliable, fast-response counter-drone solution requiring minimal human intervention, significantly enhancing safety and effectiveness in high-risk environments.

